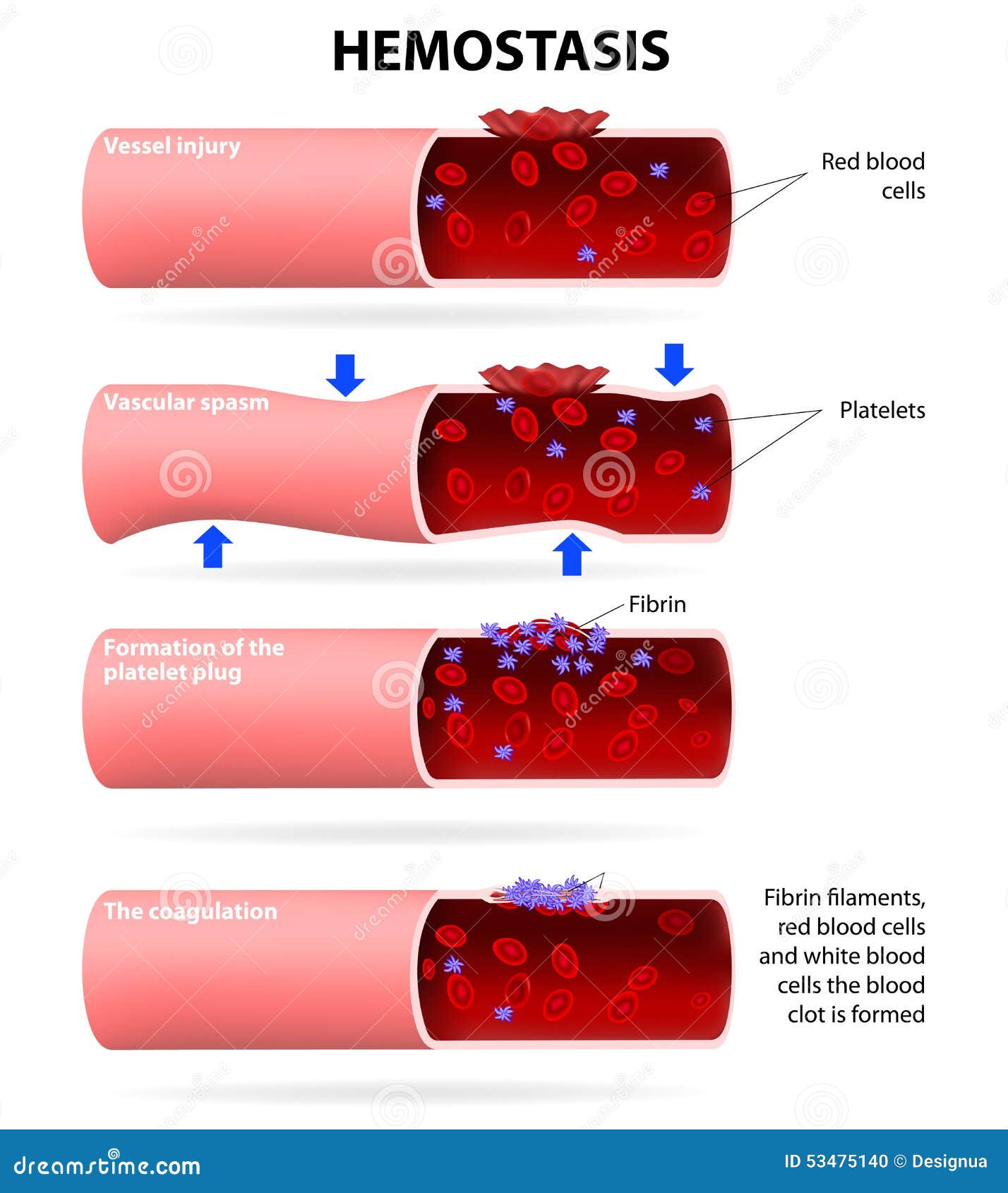
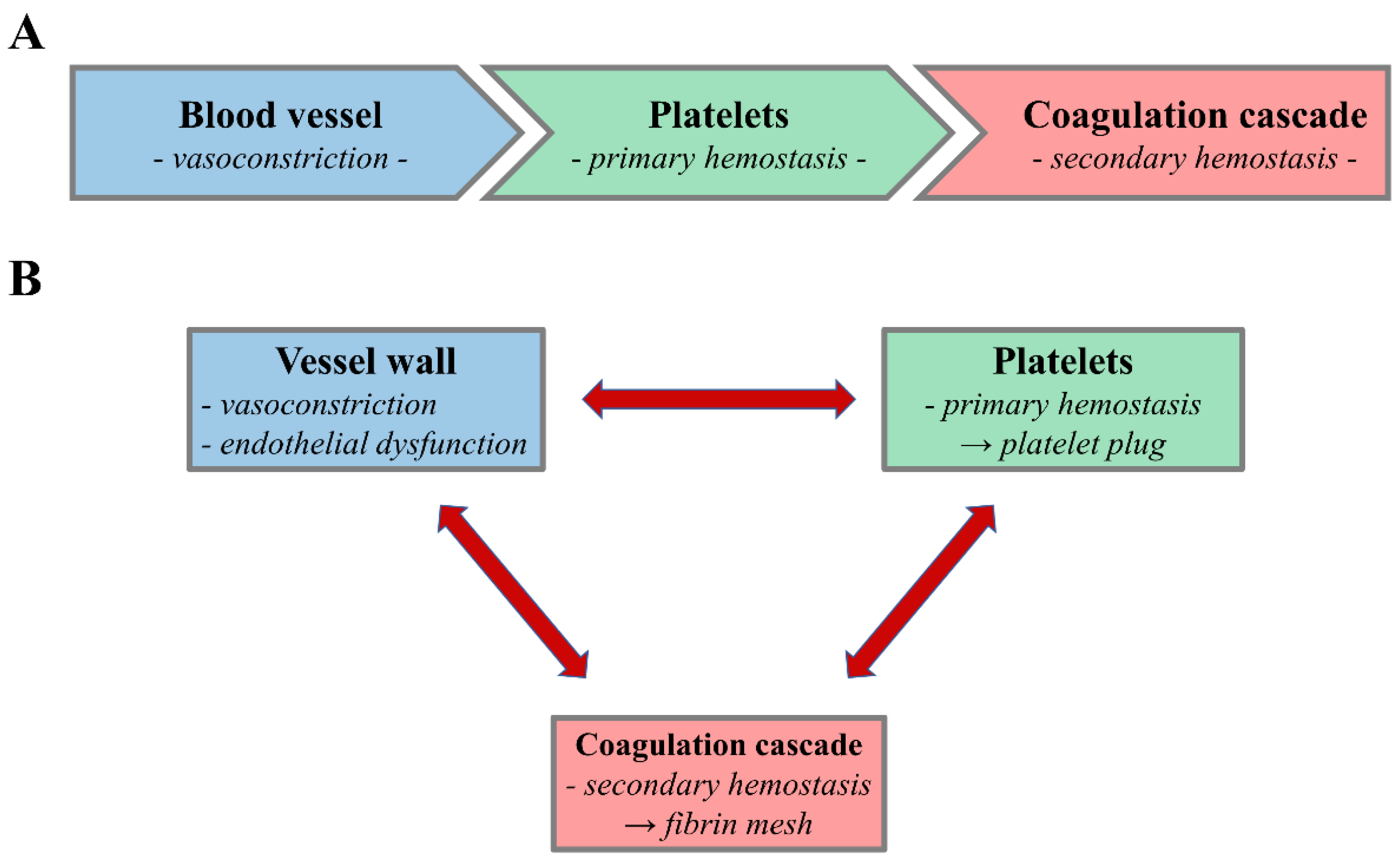
Let’s take a closer look at each of these processes. Hemostasis involves three basic steps: The goal of this review is to briefly summarize the two primary pathways of hemostasis, primary hemostasis and secondary hemostasis, as well as to summarize anticoagulant mechanisms … [1] this clot seals the injured area, controls and … It’s a delicate balance between preventing blood loss and avoiding excessive clotting. Overview of hemostasis - etiology, pathophysiology, symptoms, signs, diagnosis & prognosis from the merck manuals - medical professional version. · hemostasis is the physiological process of stopping bleeding (hemorrhage). It protects the body from blood loss and exsanguination and restores blood circulation within the … Hemostasis is the physiological process by which bleeding ceases. This reaction stops bleeding and allows your body to start repairs on the injury. · hemostasis facilitates a series of enzymatic activations that lead to the formation of a clot with platelets and fibrin polymer. · hemostasis is defined as the body’s way of stopping bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. Vascular spasm, the formation of a platelet plug, and coagulation, in which clotting … In biology, hemostasis or haemostasis is a process to prevent and stop bleeding, meaning to keep blood within a damaged blood vessel (the opposite of hemostasis is hemorrhage). · the mechanism of hemostasis involves 3 main processes – primary hemostasis, secondary hemostasis and fibrinolysis. Hemostasis (hee-muh- stay- sis) is your body’s normal reaction to an injury that causes bleeding.
Hemostasis Pathway Selection: Simple Steps To Master
Let’s take a closer look at each of these processes. Hemostasis involves three basic steps: The goal of this review is to briefly summarize the...